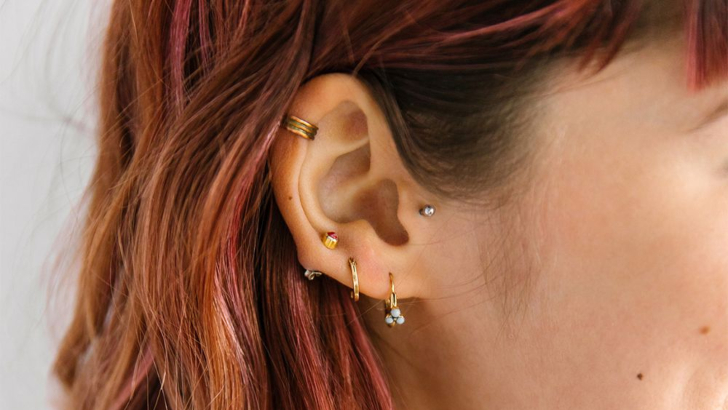From your nose to your toes, do you know how the body works? Take these quizzes to find out!
Where the nose connects to the throat are a set of glands that often disappear by adulthood. What are these glands called?
Adenoids
The adenoids are a mass of soft tissue behind the nasal cavity. Like lymph nodes, adenoids are part of the immune system and are made of the same type of tissue (lymphoid tissue). We all have adenoids at birth and in childhood, but as we head into adolescence they start to shrink. By adulthood, most people’s adenoids have disappeared.
The “fontanelle” sounds like fancy hotel on the South of France, but it’s actually what feature of human anatomy?
The soft spot on a baby’s head
The clear layer on the eye
Another name for the gallbladder
The soft spot on a baby’s head
Fontanelles are the soft spots on an infant’s head where the bony plates that make up the skull have not yet come together. It is normal for infants to have these soft spots, which can be seen and felt on the top and back of the head. Fontanelles that are abnormally large may indicate a medical condition.
In the parlance of human anatomy – which everyone should speak – what does the word “proximal” refer to?
The left side of the body
Closer to the body’s center
Something that can be removed
Closer to the body’s center
Proximal means that the structure is closer to a point of attachment, while lateral refers to a structure being away from the middle of the body. The opposing term for proximal is distal, meaning away from the point of attachment, and the opposing term for lateral is medial, meaning toward the center line.
Which of the following is the name for the yellowish pigment made during the normal breakdown of red blood cells that passes through the liver?
Bilirubin
Bilirubin is a yellowish pigment that is made during the normal breakdown of red blood cells. Bilirubin passes through the liver and is eventually excreted out of the body. Higher than normal levels of bilirubin may indicate different types of liver or bile duct problems.
Fingerprints are an odd phenomenon, made stranger by their utter uniqueness. According to Live Science, which of these is a possible reason that we have fingerprints?
They’re left over from feathers
To keep dirt off our hands
To improve touch perception
To improve touch perception
A fingerprint is an impression left by the friction ridges of a human finger. “People have had two ideas why people have fingerprints: that they help improve grip, and that they help improve touch perception,” said Roland Ennos, a biomechanics researcher and visiting professor of biology at the University of Hull in the United Kingdom.
What is the name for a “circular muscle that normally maintains constriction of a natural body passage and which relaxes as required by normal physiological functioning”?
Sphincter
Sphincters are circular muscles that serve as valves to open and close certain parts of the body. For example, the digestive system has several sphincters that regulate the passage of fluid and food from the mouth to the stomach, through the intestines, and out the anus.
There’s nothing funny about Vitreous Humor. In fact, it’s a necessary gel-like substance that keeps what body part working well?
Eye
The vitreous humor is a transparent, colorless, gel-like substance located in the posterior chamber of the eye. It helps maintain the round shape of the eye and can also help with vision clarity and shock absorbance. With aging, the vitreous humor undergoes vitreous degeneration, acquiring a thinner liquid consistency.
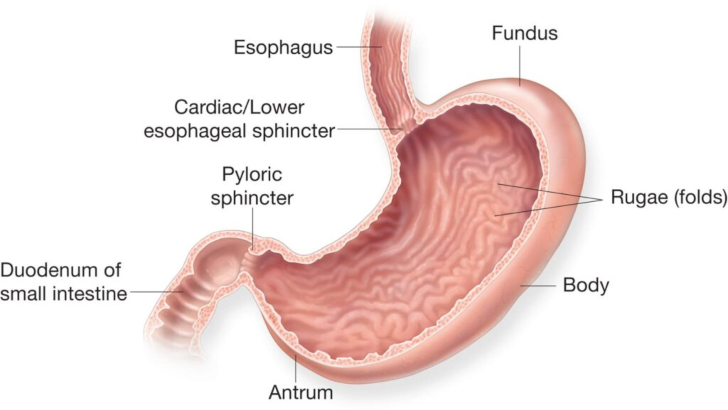
Though it has a weird name, the duodenum has a pretty important job in your body. What does it do?
Circulates blood from your heart
Breaks down food
The duodenum is the first part of the small intestine. The main role of the duodenum is to complete the first phase of digestion. In this section of the intestine, food from the stomach is mixed with enzymes from the pancreas and bile from the gallbladder. The enzymes and bile help break down food.
When we swallow food, which of the following serves as a protective flap to make sure none of it enters your windpipe?
Epiglottis
When you swallow, a flap called the epiglottis moves to block the entrance of food particles into your larynx and lungs. The muscles of the larynx pull upward to assist with this movement. They also tightly close during swallowing. That prevents food from entering your lungs.
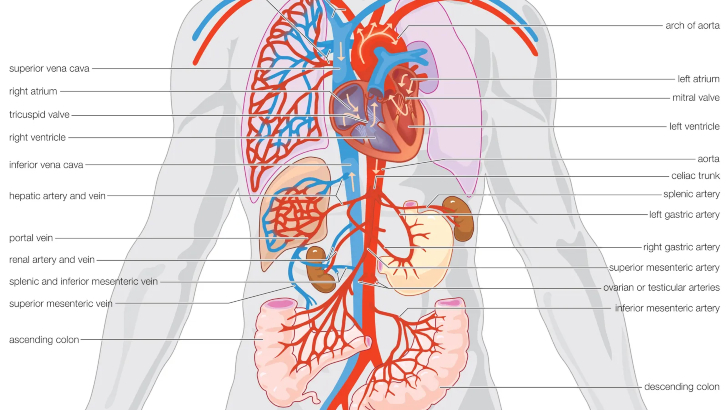
The human body has about 20 main arteries. Which of the following arteries bring unfiltered blood from the aorta to the kidneys?
Renal arteries
The renal arteries are part of the circulatory system. They carry large amounts of blood from the aorta (the heart’s main artery) to the kidneys.
Among the weirdest thing about the human body is that even as we stop growing, parts of us keep going. Which of these body parts grows all the way until we die?
Ears
Our noses and ears are unique compared to the rest of our bodies because they’re composed of soft tissue enveloped in cartilage. And it’s this soft tissue that keeps growing throughout our entire lives. “When you look at someone when they’re 80 vs. when they’re 20, they’ll have more cells in their ears and nose,” Dr.
Borborygmus is a weird bodily phenomenon that we’ve all experienced at once time or another. What is the more common way of describing borborygmus?
Stomach growling
Borborygmi refers to the sound that the stomach and intestines make as food, fluids, and gas move through them. The stomach and intestinal walls produce rumbling sounds during peristalsis, when they contract and relax to propel the food or fluids forward.
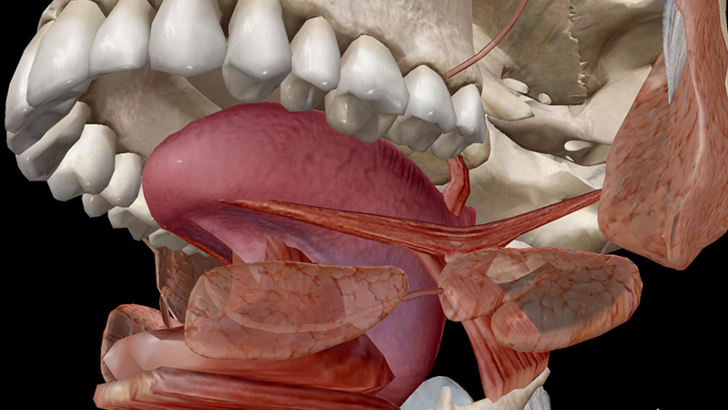
What is the term for that odd fold of mucous membrane located under the center portion of your tongue that anchors it in your mouth?
Frenulum
The lingual frenulum is a fold of mucus membrane that’s located under the center portion of your tongue. If you look in the mirror and lift up your tongue, you’ll be able to see it. The lingual frenulum helps to anchor your tongue in your mouth. It also works to stabilize the movements of the tongue.
People who study anatomy have to learn all sorts of fancy words that are used to describe simple stuff. What is the layperson’s term for adipose tissue?
Fat
Adipose tissue, also known as fat tissue or fatty tissue, is a connective tissue that is mainly composed of fat cells called adipocytes.
When you cry, there’s a gland responsible for that. Which of the following glands in the human body is responsible for the production of tears?
Lachrimal
According to the American Academy of Ophthalmology (AAO), you make 15 to 30 gallons of tears every year. Your tears are produced by lacrimal glands located above your eyes. Tears spread across the surface of the eye when you blink.
The human body part known as the “axilla” rhymes with gorilla. What does the axilla refer to?
Armpit
Axilla: This part of the human body rhymes with gorilla and can smell just as bad. (No offense to any gorillas reading today’s column.) It’s your armpit.
You have two “popliteal fossa” in your body. What couldn’t you do if you didn’t have them?
Bend your knee
The Popliteal Fossa is a diamond-shaped space behind the knee joint. It is formed between the muscles in the posterior compartments of the thigh and leg. This anatomical landmark is the major route by which structures pass between the thigh and leg.
The thinnest skin on your body is on the bottom of your feet. Where can you find the thinnest skin?
Eyelids
Epidermis varies in thickness throughout the body depending mainly on frictional forces and is thickest on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet, and thinnest in the face (eyelids) and genitalia.
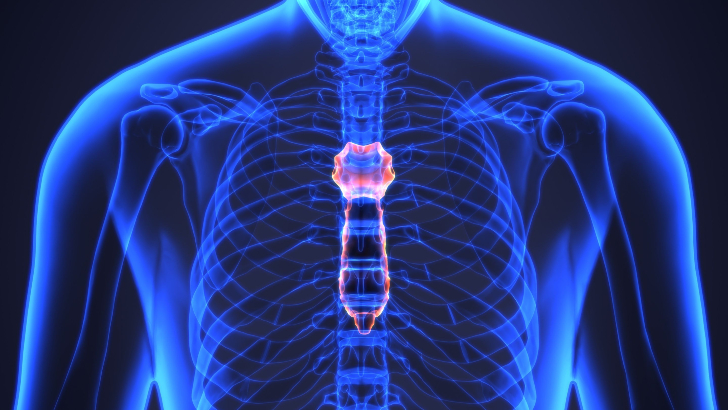
The manubrium, gladiolus, and xiphoid process are the three constituents of what part of the human body?
Sternum
The sternum is a partially T-shaped vertical bone that forms the anterior portion of the chest wall centrally. The sternum is divided anatomically into three segments: manubrium, body, and xiphoid process.
You’ve heard of Hammertoe, but what does it mean if someone has “Morton’s Toe”?
Big toe is shorter than second toe
Big toe is shorter than second toe
Rubbing from a tight shoe can also cause a Morton’s toe to progress into a hammer toe, which is when your big toe curls inward and becomes effectively shorter. Rubbing from a tight shoe can also cause a Morton’s toe to progress into a hammer toe, which is when your big toe curls inward and becomes effectively shorter.
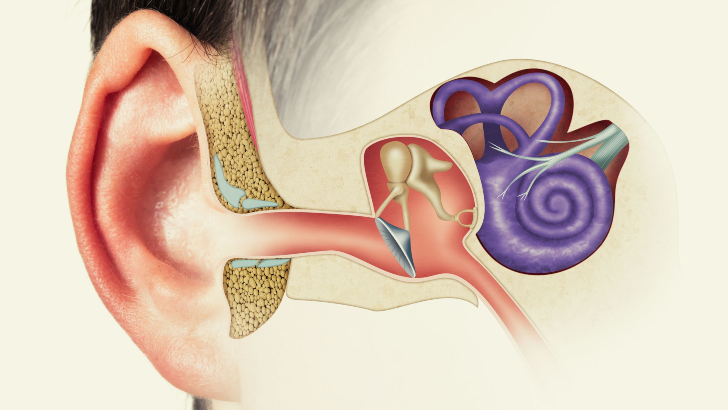
The malleus, incus, stapes are tiny bones in the ear and are collectively known as the “auditory” what?
Ossicles
The ossicles (also called auditory ossicles) are three bones in either middle ear that are among the smallest bones in the human body. They serve to transmit sounds from the air to the fluid-filled labyrinth (cochlea).
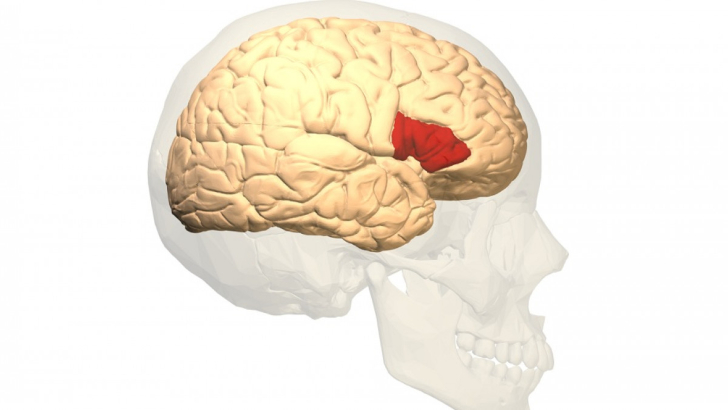
Named in honor of a French doctor, the so-called Broca Area in the brain is most closely linked to which of the following human functions?
Speech
Broca’s area is a key component of a complex speech network, interacting with the flow of sensory information from the temporal cortex, devising a plan for speaking and passing that plan along to the motor cortex, which controls the movements of the mouth.
What is the term for the involuntary constriction and relaxation of the muscles that cause food to move down the esophagus?
Peristalsis
Alternating contraction and relaxation of these muscles is called peristalsis. Peristaltic waves push the swallowed bolus down the esophagus. In the stomach, peristalsis churns swallowed food, mixing it with gastric juices
What would be the more scientific way to say that you “knuckle-punched” somebody?
You clavicule-punched them
You condyle-punched them
Condyle is an anatomy term referring to “an articular prominence of a bone”. In other words, the bones that stick out when you form a knuckle are condyles. It’s really the condyles that do the most damage to the person being punched.
We have so many weird parts, it’s hard to know where to begin. What part of our body is also considered a “muscular hydrostat”?
Tongue
The tongue is all muscle, but not just one muscle – it’s made up of 8 different muscles that intertwine with each other creating a flexible matrix, much like an elephant’s trunk. It’s called a muscular hydrostat, and the tongue muscles are the only muscles in the human body that work independently of the skeleton.
As described by a pediatric doctor at Vanderbilt Children’s Hospital in Nashville, one weird fact about the human body is that kids grow fastest during which season?
Summer
According to this doctor’s study, kids grow most quickly in the summer and most slowly in the fall. Truly just an odd phenomenon, the physicians admits: “We don’t have a good explanation for it.”
The process known as angiogenesis refers to the formation and regeneration of what part of the human body?
Blood cells
Angiogenesis is the formation of new blood vessels from existing ones, in contrast to vasculogenesis, where new primitive blood vessels are formed from angioblasts.
The displacement of what tiny particles in the ear is known to be responsible for the feeling of vertigo or dizziness?
Calcium Carbonate
Often the cause of vertigo is the displacement of small calcium carbonate crystals, or canaliths, within the inner ear. Canalith repositioning procedure (CRP) is a method to remove these crystals trapped in the ear’s semicircular canal.
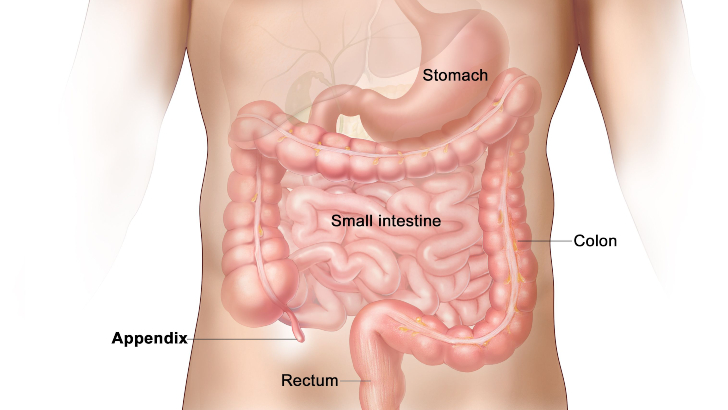
We all know the appendix is an odd organ, seemingly completely unnecessary. According to recent research, however, what purpose might the appendix serve?
As a way of balancing out weight of other organs
To lessen the effects of allergies
As a vessel to hold healthy bacteria
As an “understudy” pancreas
As a vessel to hold healthy bacteria
Researchers deduce that the appendix is designed to protect good bacteria in the gut. That way, when the gut is affected by a bout of diarrhea or other illness that cleans out the intestines, the good bacteria in the appendix can repopulate the digestive system and keep you healthy.
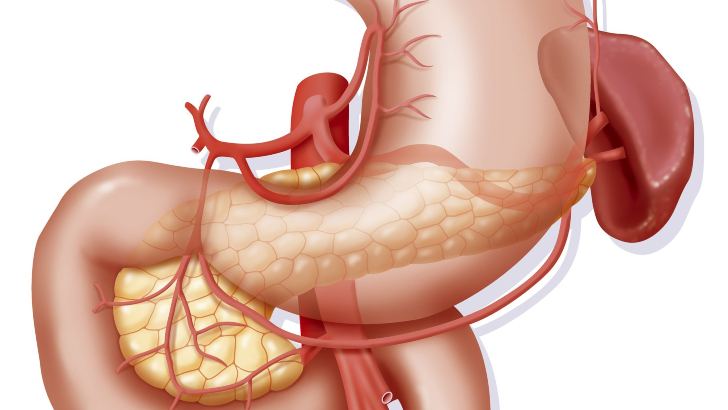
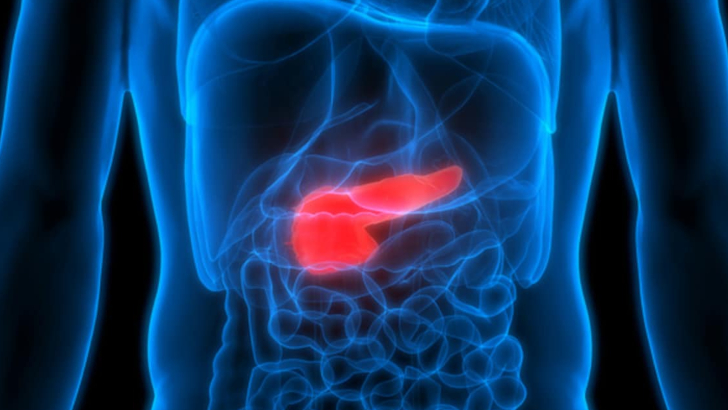
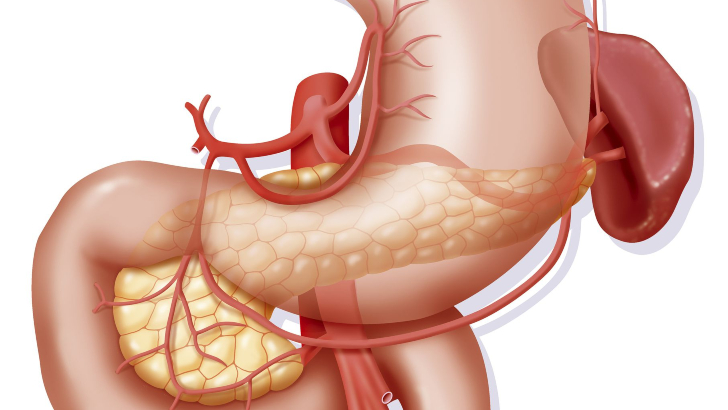
The islets of Langerhans is not an archipelago off the coast of Scandinavia, but a cluster of cells in which human organ?
Pancreas
Islets of Langerhans, also called islands of Langerhans, irregularly shaped patches of endocrine tissue located within the pancreas of most vertebrates.
In most of the world, our normal body temperature is measured in Celsius, not Fahrenheit. What is considered a normal body temperature?
37 degrees Celsius
Normal body temperature is considered to be 37°C (98.6°F); however, a wide variation is seen.
If you injured your “hallux,” what might you have to wear for a while until it healed?
A boot on your foot
Hallux rigidus, sometimes called turf toe or stiff big toe, is when you have big toe pain. The pain can make it hard to walk or even stand. Often, nonsurgical treatments, such as properly fitting shoes, can help.
It’s odd that our knuckles evolved in such a way that they can be cracked. What’s happening that creates the sound of a knuckle cracking?
Your knuckles saying “ow!”
Tendon snapping in and out of place
Gas bubbles bursting
The characteristic pop can be explained by three mathematical equations, say researchers in the US and France. Their model confirms the idea that the cracking sound is due to tiny bubbles collapsing in the fluid of the joint as the pressure changes.
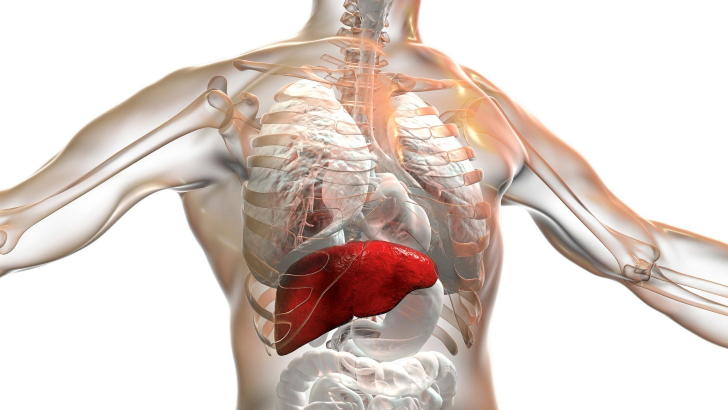
Some of our strangest body parts work on many levels. Which of the following organs has been discovered by scientists to have more than 500 functions?
Liver
The liver is classed as a gland. This vital organ carries out more than 500 roles in the human body. It is the only organ that can regenerate.
The way the human body works can sometimes be random. Case in point: About 1 out of every 200 people are born with an extra what?
Rib
Each adult has 206 bones, 24 of which are ribs (12 on each side), but approximately one out of every 200 people have an extra rib. This rib is referred to as the cervical rib. A cervical rib is present at birth and it forms above the first rib, growing at the base of the neck, just above the collarbone.
Aging is odd – and unsettling. By the time the average person turns 60, what have they lost about 50% of?
Taste buds
As we age, the number of taste buds that we have decreases. This usually begins to occur in our 40s if we’re female or in our 50s if we’re male. At the same time, our remaining taste buds also begin to shrink, or atrophy, and do not function as well.
If you put a stud on the piece of cartilage on the front of your ear – where it attaches to your head – what would you have pierced?
Tragus
The tragus is a small pointed eminence of the external ear, situated in front of the concha, and projecting backward over the meatus. It also is the name of hair growing at the entrance of the ear. Its name comes the Ancient Greek tragos (τράγος), meaning ‘goat’, and is descriptive of its general covering on its under surface with a tuft of hair, resembling a goat’s beard.
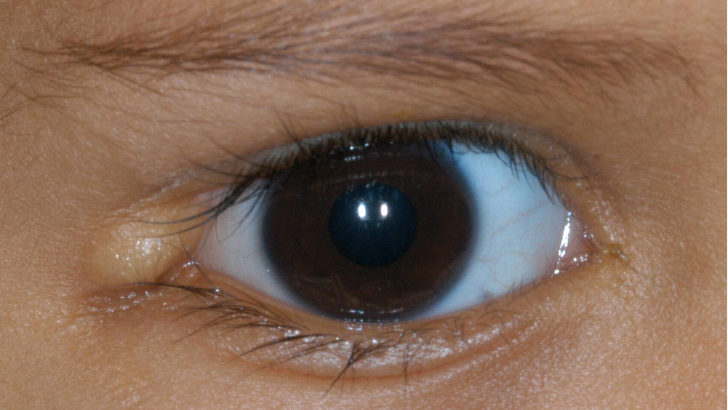
In the category of “they have a name for everything,” what is the scientific term for the corner where your upper eyelid meets your lower one?
Canthus
The canthus is either corner of the eye where the upper and lower eyelids meet. More specifically, the inner and outer canthi are, respectively, the medial and lateral ends/angles of the palpebral fissure.
Though it has a weird name, the duodenum has a pretty important job in your body. What does it do?
Circulates blood from your heart
Breaks down food
The duodenum, the first and shortest section of the small intestine, is a key organ in the digestive system. The small intestine’s most important function is to digest nutrients and pass them into the blood vessels—located in the intestinal wall—for absorption of the nutrients into the bloodstream.
The scientific term for the vestigial tailbone all humans have is an odd-sounding word. Which of these spellings is the correct one?
Coccyx
Although the tailbone is considered vestigial (or no longer necessary) in the human body, it does have some function in the pelvis. For instance, the coccyx is one part of a three-part support for a person in the seated position.
YES, you failed!!! 
But we know you can do better next time…
Oh no, we are this close!!!
Try a little harder next time…
Well done!!! 
You nailed it…
[giveaway id=12098]